Publikationen
Ausgewählte Publikationen
Hier finden Sie ausgewählte Publikationen aus den letzten Jahren. Eine ausführliche Liste der Publikationen finden Sie auf der Google Scholar oder DBLP Seite von Stefan Schneegaß.
Art der Publikation: Beitrag in Zeitschrift
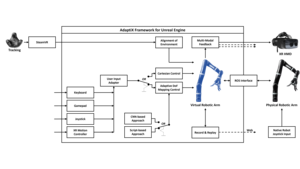
AdaptiX – A Transitional XR Framework for Development and Evaluation of Shared Control Applications in Assistive Robotics
- Autor(en):
- Pascher, Max; Goldau, Felix Ferdinand; Kronhardt, Kirill; Frese, Udo; Gerken, Jens
- Titel der Zeitschrift:
- Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact.
- Jahrgang (Veröffentlichung):
- 8 (2024)
- Heftnummer:
- EICS
- Ort(e):
- New York, NY, USA
- Schlagworte:
- assistive robotics, human–robot interaction, shared user control, augmented reality, virtual reality, mixed reality, visual cues
- Digital Object Identifier (DOI):
- doi:10.48550/ARXIV.2310.15887
- Volltext:
- AdaptiX – A Transitional XR Framework for Development and Evaluation of Shared Control Applications in Assistive Robotics (1.10 MB)
- Zitation:
- Download BibTeX
Kurzfassung
With the ongoing efforts to empower people with mobility impairments and the increase in technological acceptance by the general public, assistive technologies, such as collaborative robotic arms, are gaining popularity. Yet, their widespread success is limited by usability issues, specifically the disparity between user input and software control along the autonomy continuum. To address this, shared control concepts provide opportunities to combine the targeted increase of user autonomy with a certain level of computer assistance. This paper presents the free and open-source AdaptiX XR framework for developing and evaluating shared control applications in a high-resolution simulation environment. The initial framework consists of a simulated robotic arm with an example scenario in Virtual Reality (VR), multiple standard control interfaces, and a specialized recording/replay system. AdaptiX can easily be extended for specific research needs, allowing Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) researchers to rapidly design and test novel interaction methods, intervention strategies, and multi-modal feedback techniques, without requiring an actual physical robotic arm during the early phases of ideation, prototyping, and evaluation. Also, a Robot Operating System (ROS) integration enables the controlling of a real robotic arm in a PhysicalTwin approach without any simulation-reality gap. Here, we review the capabilities and limitations of AdaptiX in detail and present three bodies of research based on the framework. AdaptiX can be accessed at adaptix.robot-research.de.
